Best ROCE Assignment Help
JCPenney operates a chain of retail department stores, selling apparel, shoes, jewelry, and home furnishings.
It also offers most of its products through catalog distribution. During fiscal Year 5, it sold Eckerd Drugs,
a chain of retail drugstores, and used the cash proceeds, in part, to repurchase shares of its common stock.
Exhibit 4.27 presents selected data for JCPenney for fiscal Year 3, Year 4, and Year 5.

- Calculate the rate of ROA for fiscal Year 3, Year 4, and Year 5. Disaggregate ROA into the profit
margin for ROA and total assets turnover components. The income tax rate is 35%. - Calculate the rate of ROCE for fiscal Year 3, Year 4, and Year 5. Disaggregate ROCE into the profit
margin for ROCE, assets turnover, and capital structure leverage components. - Suggest reasons for the changes in ROCE over the three years.
- Compute the ratio of ROCE to ROA for each year.
- Calculate the amount of net income available to common stockholders derived from the use of financial
leverage with respect to creditors’ capital, the amount derived from the use of preferred shareholders’
capital, and the amount derived from common shareholders’ capital for each year. - Did financial leverage work to the advantage of the common shareholders in each of the three years?
Explain

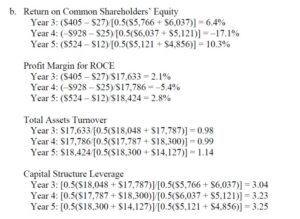
JCPenney (Penney) operated at a net loss in Year 4. The problem does not provide data on cost
of goods sold, selling and administrative expenses, or other expenses that might explain the net loss.
One suspects that Eckerd Drugs might have operated unprofitably or that Penney recognized asset
impairment or restructuring charges that resulted in a net loss.
Note that the assets turnover did not change much, indicating that the explanation for the net loss lies in the profit margin for ROA and ROCE. The ROCE increased between Year 3 and Year 5, the result of an improved profit margin for ROA and ROCE and increased assets turnover.
Again, one suspects that the sales of Eckerd Drugs helped both of these financial ratios. Also, the capital structure leverage ratio increased. The increase between Year 3 and Year 4 resulted from operating at a net loss, which reduces retained earnings and shareholders’ equity. The increase between Year 4 and Year 5 likely resulted from the net effect of a reduction in debt from selling Eckerd Drugs and the stock buyback with the proceeds of the sale.



